Effective prioritization is paramount for successful product management, as it requires astute decision-making regarding feature development, problem-solving, and resource allocation in pursuit of corporate objectives. This pivotal skillset is integral to navigating the intricate web of product development constraints, such as resource limitations, market competition, and ever-changing consumer preferences. Given the perpetual influx of ideas and initiatives, prioritization can be daunting, necessitating various techniques and methodologies to optimize product management strategies. Product prioritization is an important aspect of building a successful product. Leaders in product management often say that if you are facing a prioritization problem, it could be a strategy problem.
This blog post is a continuation of our previous post on “THE ART OF PRIORITIZATION IN PRODUCT MANAGEMENT: BALANCING SHORT-TERM AND LONG-TERM GOALS“. In that post, we discussed the importance of balancing short-term and long-term goals while prioritizing features for a product. As a follow-up, we will delve into some prioritization techniques that can help product managers make informed decisions about which features to build and how to allocate resources to achieve their company’s goals.
Product Management Pritotization Techniques
-
Value vs Efforts
As a product manager, your ultimate goal is to deliver the best possible product to your customers while achieving your company’s objectives. However, with limited resources and an abundance of ideas, prioritization is key to ensuring that you’re making the right decisions. The value vs. effort method is one of the most effective techniques for prioritizing ideas. By ranking ideas based on their impact on the company’s goals and the difficulty of implementation, you can make informed decisions about which features to prioritize.
For example, let’s consider the example of a social media platform that wants to increase user engagement. The product team may develop several ideas, such as adding a chat feature, creating a recommendation algorithm, or adding a feature to allow users to share their favorite posts with their friends. The team can use the value vs. effort technique to decide which of these ideas to prioritize.
Adding a chat feature may have a high impact on user engagement, but it could be complex and time-consuming to implement. Creating a recommendation algorithm could also have a high impact, but it might require a significant amount of effort from the development team. On the other hand, allowing users to share their favorite posts with their friends could be a relatively easy feature to implement, but it may not have as significant an impact on user engagement. Using the value vs. effort chart, the product team can quickly see which ideas are high priority and which ones are low priority. This technique can help the team make data-driven decisions and ensure that they are focusing on the most impactful features.
This technique is often visualized with a chart like the one below:
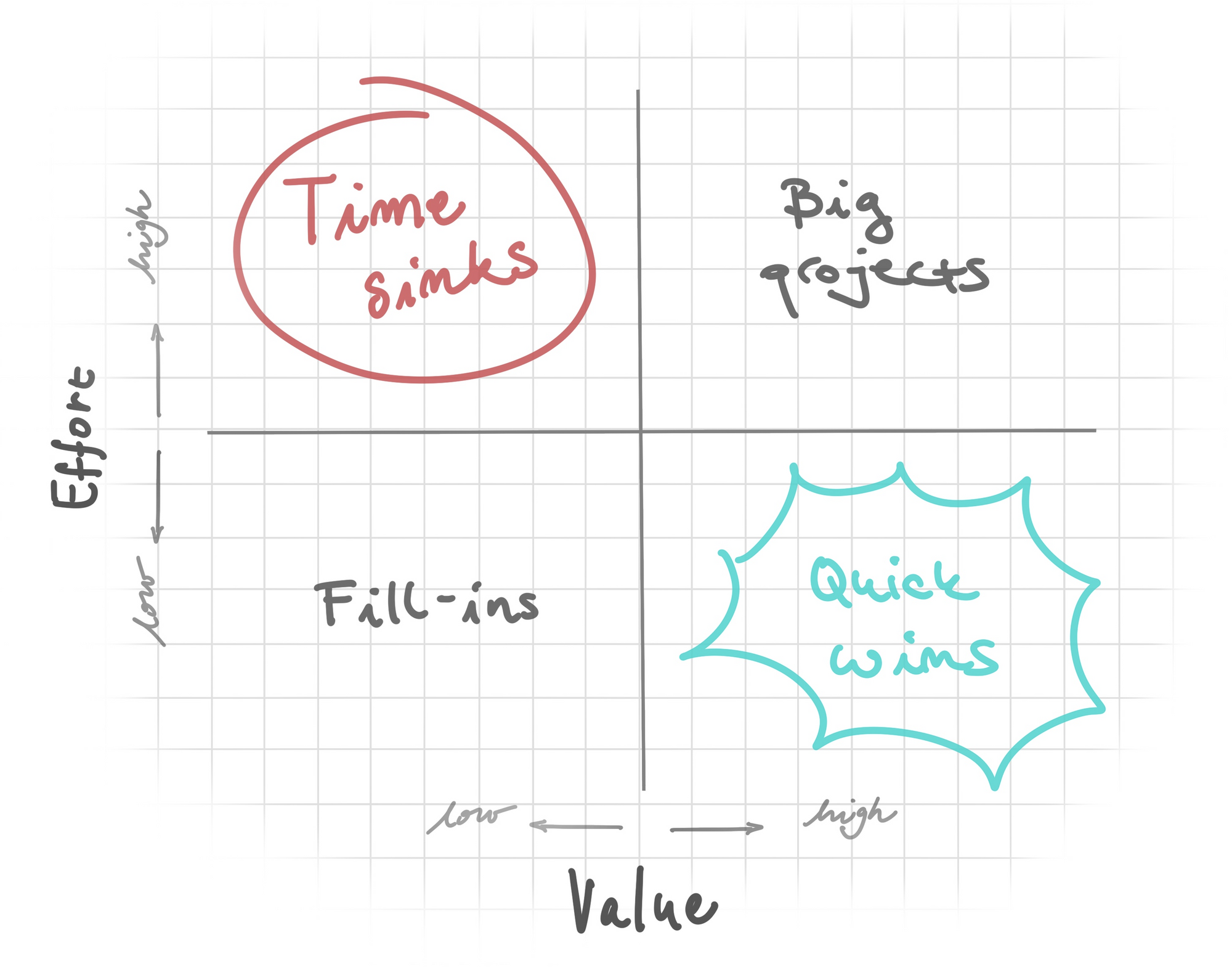
Features in the top right quadrant have high value and low effort, and are therefore high priority. Features in the bottom left quadrant have low value and high effort, and are low priority. Features in the bottom right quadrant have low value and low effort, and can be deprioritized. Features in the top left quadrant have high effort and high value, and require more analysis to determine their priority.”
While this method has its benefits, there are also drawbacks to consider. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of the Value vs. Effort technique.
Pros:
- Value vs. Effort technique is a simple and easy-to-understand method for prioritizing features or problems.
- It provides a clear visualization of the potential impact and effort required for each idea.
- The quadrant chart helps product managers to focus on high-value and low-effort ideas, which can lead to faster and more impactful product improvements.
- It allows product managers to compare and prioritize different ideas in a structured way.
Cons:
- The value and effort can be subjective and difficult to measure accurately. Different stakeholders may have different opinions on what constitutes value and effort.
- This method does not take into account the dependencies between features or problems. A feature that has high value and low effort in isolation may become more complex and require more effort when combined with other features.
- It does not consider the strategic goals or long-term vision of the company. Some ideas may have low value or high effort in the short term but may be critical to achieving the company’s long-term objectives.
- There is a risk of over-reliance on this method, which may lead to neglecting other important factors such as market research, customer feedback, or competitive analysis.
2. Kano Model
The Kano model is a framework for categorizing features based on their impact on customer satisfaction. The model has three categories: must-haves, performance attributes, and delighters. Must-haves are features that customers expect, and their absence will result in dissatisfaction. Performance attributes are features that increase satisfaction as they improve, and their absence does not result in dissatisfaction. Delighters are features that exceed expectations and result in high satisfaction. It is a technique for categorizing features based on their impact on customer satisfaction, and it has become a staple in the product management world.
The Kano Model is a valuable tool for product managers to identify which features are critical to customer satisfaction. For example, let’s consider a mobile phone company that is developing a new device. One of the must-have features for a smartphone is the ability to make phone calls and send text messages. If this feature is not included, customers will be dissatisfied with the product. Performance attributes for a smartphone may include battery life, camera quality, and processing speed. Improving these features can increase customer satisfaction, but their absence does not necessarily result in dissatisfaction. Delighters for a smartphone may include features such as facial recognition, gesture controls, or augmented reality capabilities. While these features can lead to high customer satisfaction, they are not expected by customers and may not be a priority for the company. By using the Kano Model, product managers can prioritize features based on their impact on customer satisfaction and focus their resources on the most critical areas.
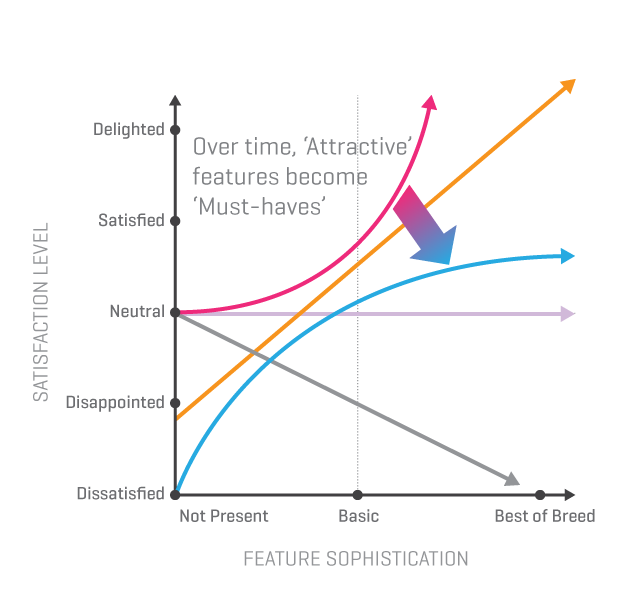
Features in the must-haves category are high priority because their absence will result in customer dissatisfaction. Features in the performance attributes category can be prioritized based on their impact on customer satisfaction. Features in the delighters category are low priority because they are not expected by customers.”
The Kano model is a popular framework for prioritizing features based on their impact on customer satisfaction. While this method can be effective in helping product managers understand how to allocate resources to maximize customer satisfaction, there are both pros and cons to its use. In this section, we will explore the benefits and limitations of the Kano model for product managers.
Pros:
- The Kano Model focuses on customer satisfaction, which can help product managers to create products that meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
- It helps product managers to identify and prioritize features that are critical to customer satisfaction.
- The model is easy to understand and apply, and the chart provides a clear visualization of feature categories.
- The Kano Model is a useful tool for market research and can help product managers to gather feedback from customers.
Cons:
- The model is based on customer expectations and may not account for new or innovative features that customers may not be aware of.
- The categories are not always clear-cut and may be subject to interpretation.
- The Kano Model does not take into account the cost or effort required to implement each feature.
- The model is primarily focused on customer satisfaction and does not account for other important factors such as market demand, competition, or company goals.
Overall, the Kano Model can be a useful tool for prioritizing features based on customer satisfaction, but it should be used in conjunction with other methods and considerations to ensure a well-rounded approach to product management.
3. RICE
RICE is a prioritization framework that takes into account the reach, impact, confidence, and effort of a feature. Reach is the number of users who will be impacted by the feature. Impact is the degree to which the feature will impact the company’s goals. Confidence is the level of certainty the team has in the estimates. Effort is the level of effort required to implement the feature. By considering the potential reach of the feature, the impact it will have on the company’s goals, the team’s confidence in their estimates, and the effort required to implement the feature, product managers can make informed decisions about which features to prioritize.
Overall, the RICE framework provides a comprehensive and data-driven approach to feature prioritization. By considering reach, impact, confidence, and effort, the framework helps product managers make informed decisions about which features to prioritize. However, like any method, the RICE framework has its pros and cons.
One of the key benefits of the RICE framework is its focus on impact. Unlike other frameworks that may prioritize low-hanging fruit or quick wins, the RICE framework helps product managers identify features that will have the greatest impact on the company’s goals. For example, if a social media platform wants to increase user engagement, the RICE framework would prioritize features that increase engagement, such as a new commenting system or a feature that allows users to share content more easily.
Another benefit of the RICE framework is its consideration of reach. By prioritizing features that will impact a large number of users, product managers can ensure that they are making the most of their resources and addressing the needs of their user base as a whole.
However, one of the challenges of the RICE framework is the difficulty of accurately measuring and estimating reach, impact, and effort. For example, estimating the impact of a new feature on the company’s goals can be difficult without access to relevant data or prior experience with similar features. Additionally, the level of effort required to implement a feature may be underestimated, leading to unrealistic expectations for delivery timelines.
Overall, the RICE framework is a useful tool for product managers, but it is important to use it in conjunction with other methods, such as user feedback and market research, to ensure a holistic approach to feature prioritization.
More methods would be added subsequently.









